BIOS/UEFI Setup Guide: Boot from a CD, DVD, USB Drive or SD Card
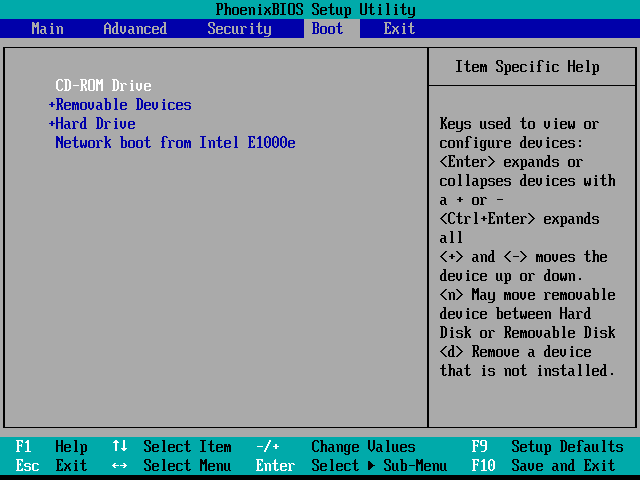
Booting from a USB or CD/DVD drive can be tricky depending on your computer’s BIOS / UEFI setup. In this guide, we’ll break it down step-by-step.
Windows runs on thousands of computer configurations, but installing a new operating system like Windows 10 on the variety of configurations that exist is another thing. The steps may be different depending on whether your computer has an existing Windows 10 installation on it, an earlier version of Windows on it or a completely different operating system on it, like macOS or Linux. In each case, installing Windows 10 relies on booting from a device other than your main hard disk drive (HDD) or solid state drive (SSD). To do that, you need to access the BIOS or UEFI setup page. Sometimes, this is easier said than done.
In this guide, we’ll walk through the basic steps that apply to most scenarios. Then, we’ll discuss some troubleshooting and alternate methods, in case the simple approach doesn’t work for you.
How-to Summary: Boot Your Computer from a CD/DVD/USB/SD Drive
- BIOS vs. UEFI: What’s the Difference? Optional. In case you want some background info on what the heck UEFI is and why it makes things difficult.
- How to Access BIOS / UEFI Setup Screen. Includes the keyboard commands you need to access the BIOS or UEFI setup screen.
- Navigate BIOS / UEFI Setup Screen. Finding your way around without a typical keyboard/mouse interface.
- How to Change Boot Order in BIOS / UEFI. These are the settings you need to change in BIOS / UEFI to allow your PC to boot from a USB or CD.
- Booting from a USB/CD/DVD Drive or SD Card. Once you’ve configured your BIOS / UEFI correctly, here’s what to do.
Best case scenario, those steps will get you up and running. If not, see our Troubleshooting section. This includes details for changing the boot order on a Microsoft Surface device and booting from another device on a Mac.
Note: Once you master the steps to boot your computer from a USB or CD/DVD, you can use this to boot other operating systems or bootable live environments on your machine.
BIOS vs. UEFI: What’s the Difference?
Each computer, whether it’s a Dell, HP, Acer or even a custom-built system, is an island unto itself before Windows 10 (or some other operating system) starts. Since the 1980s, hardware vendors have worked together to standardize around common access routines and commands for managing your BIOS Boot Options. The BIOS, which stands for Basic In Output System, is a critical bit of low-level code stored in nonvolatile memory that your computer uses to manage your hardware and load Windows 10 or another operating system.
A new standard called UEFI or Universal Extensible Firmware Interface came online a decade ago and became the standard for new PCs and devices preinstalled with Windows 8 or later. UEFI offers more advanced options than BIOS, with support for features such as a graphical user interface and mouse support, making it easier to configure boot and hardware settings. UEFI also supports recent security standards required by Windows 10 and previous releases such as Secure Boot, which maintains the integrity of a computer’s state and prevents malicious code from compromising your system at boot time. After decades of systems using BIOS, malware has become more sophisticated, where it is even possible for malicious code to easily infect key operating system code such as the Master Boot Record.
How to Access Your BIOS or UEFI Setup Screen
Because of the variety of brands and configurations, and the ongoing revisions to these systems, this article is not exhaustive. That said, the following provides a comprehensive list of common methods for booting into the BIOS or UEFI firmware interfaces.
To enter the BIOS, you need to press a certain key or combination of keys while your computer is booting up. Usually, your window to do this is very brief—you have to press the button when the splash screen with the manufacturer’s logo is displayed. If it seems like your computer boots too fast for you to get a chance to hit the button, you may need to disable fast startup.
Here is a list of the common functions or commands for loading the BIOS. Please note, your BIOS screen might display a hint to indicate the appropriate function key for loading the firmware. Start your computer then proceed to strike the appropriate key or command to load the BIOS. After loading the BIOS or UEFI, connect your USB media or connect the DVD install media.
| Brand / Manufacturer | Key |
| Acer (Aspire, Altos, Extensa, Ferrari, Power, Veriton, TravelMate) | F2 / Delete |
| Acer (older models) | F1 / Ctrl + Alt + Esc |
| ASRock | F2 / Delete |
| Asus | Delete |
| Biostar | Delete |
| Chaintech | Delete |
| Compaq (Deskpro, Portable, Presario, Prolinea, Systempro) | F10 |
| Compaq (older models) | F1 / F2 / F10 / Delete |
| Dell (Dimension, Inspiron, Latitude, OptiPlex, Precision, Vostro, XPS) | F2 |
| Dell (older or other models) | Ctrl + Alt + Enter / Fn + Esc / Fn + F1 / Delete / Reset twice |
| eMachines (eMonster, eTower, eOne, S-Series, T-Series) | Tab / Delete |
| eMachines (older models) | F2 |
| Foxconn | Delete |
| Fujitsu | F2 |
| Gigabyte | Delete |
| HP (Alternative, Tablet PC) | Esc / F2 / F10 / F12 |
| HP (OmniBook, Pavilion, Tablet, TouchSmart, Vectra) | F1 |
| Intel | F2 |
| Lenovo (3000 Series, IdeaPad, ThinkCentre, ThinkPad, ThinkStation) | F1 / F2 |
| Lenovo (older models) | Ctrl + Alt + F3 / Ctrl + Alt + Ins / Fn + F1 |
| MSI | Delete |
| Pegatron | F2 / F10 / Delete |
| Samsung | F2 |
| Sony | F1 / F2 / F3 |
| Toshiba | F1 / Esc |
Navigating BIOS / UEFI Setup
Each BIOS or UEFI looks different and works differently, but most share basic principles for navigation. For menu-driven BIOS or UEFI interfaces, your keyboard’s arrow keys are used to access and enter menus. The settings for configuring boot options are sometimes hidden under submenus, which you will have to navigate using these keys.
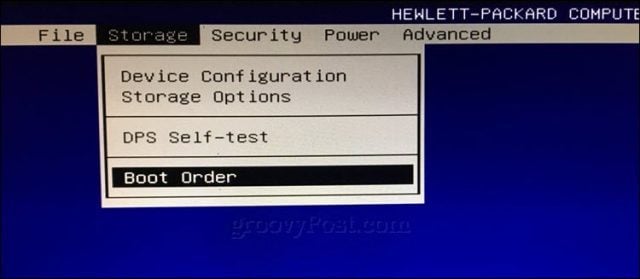

On my HP desktop, the option for changing the system’s boot order is located under Storage > Boot Order. On my other computer, an HP Elitebook, the boot order is called Boot Options located under the System Configuration tab, which uses a graphical interface. So, the experience will vary depending on the system you are using; even if they are the same brands. Navigate through these interfaces by browsing and looking for logical labels that might suggest what you are looking for – storage, boot, disks, etc.
How to Change the BIOS / UEFI Boot Order to Boot from a USB / CD Drive
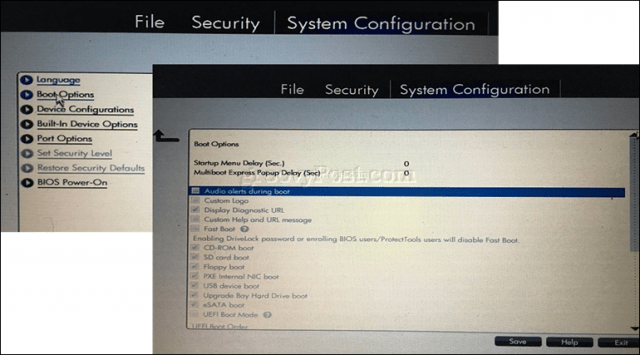

Once you’ve found the Boot Order menu, the interface will present menus displaying the structure of your boot order. Boot order determines which devices your computer will try to boot from first, second, etc. when you turn it on. Most often, your first boot device is your hard disk or SSD containing Windows 10. You can also have your DVD, CD, or USB thumb drive, set as the first boot device without it affecting Windows 10 loading into main memory. If you have a removable storage device set as your first boot device the BIOS will check if there is any attached removable storage as part of POST (Power On Self Test). If a USB thumb drive or DVD is detected, the system will prompt you to boot from it before loading any existing operating systems on the local disk.
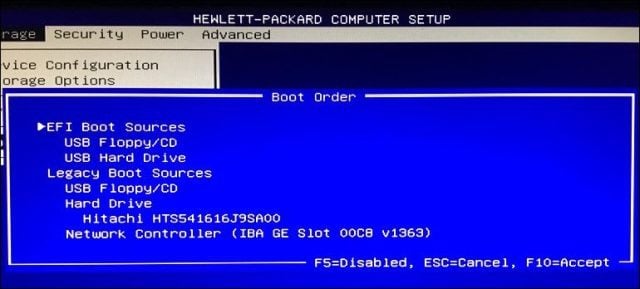

Moving through the options will require using the arrow keys. If you don’t see your connected USB device listed, choose the USB storage listed under EFI or Legacy sources. Use the down arrow key to navigate to the selection; some older BIOS interfaces will require using function keys such as F5 and F6 to navigate up and down the boot order. After selecting the appropriate option, you will need to confirm these changes; pressing F10 will usually save them. If not, read the on-screen instructions, which will identify the appropriate function key for saving or accepting changes.
Booting from a USB drive or CD/DVD
Once the desired option has been selected and confirmed, depending on the type of installation media you are using, you might see different options. USB media will immediately boot into a Windows Boot Manager, prompting selection of the architecture of Windows 10 – 32 or 64 bit – you would like to install.
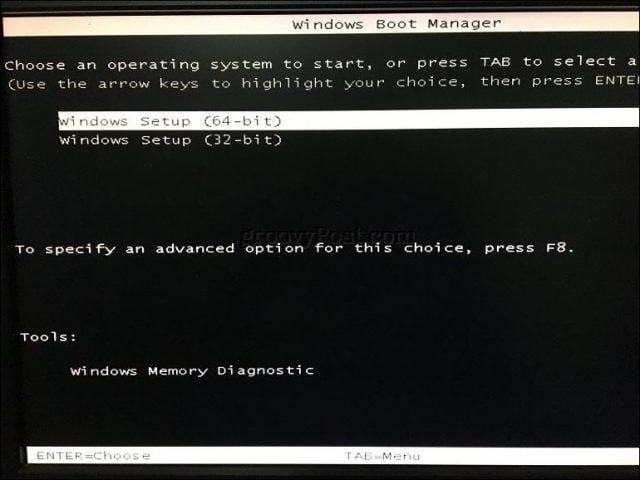

If you are installing from DVD media, Windows 10 setup will prompt you to hit any key on your keyboard to load setup.
From there, you should be home-free. As long as you created your bootable installation media correctly, the on-screen instructions should guide you through the rest of the process.
Troubleshooting Boot Options
Some systems might encounter problems when attempting to boot from removable media. If you are following the steps above to a T and you’re still having issues, look into some of the items below.
- Accessing the UEFI setup page on a Microsoft Surface device. The steps for accessing the BIOS / UEFI page on Surface devices are a bit different. See the steps below for Setting Up UEFI on a Microsoft Surface.
- Changing UEFI settings on an out-of-the-box Windows 8 or Windows 10 device. For computers that you buy with Windows 8 or Windows 10 pre-installed, it may be tricky to access the UEFI / BIOS. See the steps below for Configuring UEFI on Windows 8 or Windows 10 Computers.
- What about Mac? Apple computers support installing Windows, but they don’t have a BIOS / UEFI setup page like your typical PC. See our section on installing Windows on a Mac below.
- Make sure the bootable media was created properly. Boot issues can sometimes be attributed to how the install media was configured or prepared. For instance, on UEFI-based systems – systems designed for Windows 8 or later – preparing the install media, if downloaded from the Microsoft software page, will require using the Microsoft Media Creation Tool or a third-party utility such as Rufus.
- Enable Legacy Boot Sources. If you are installing on an older computer using BIOS, selecting the option under Legacy Boot Sources or Legacy USB will let you start Windows setup from a USB or CD drive.
- Disable Secure Boot. Security technologies included in UEFI such as Secure Boot can be a blocker and prevent the system from booting external storage sources. Disabling Secure Boot, temporarily—normally accessible under the security menu or tab—will often resolve this.
- Disable Fast Startup. If you are unable to access the BIOS, you may need to disable Fast Startup, if it is enabled.
- Resetting BIOS settings. Some BIOS / UEFI setup screens have a factory reset option. This can sometimes be a quick fix but proceed with caution. If you have your drive BitLocker encrypted with TPM enabled, this may make your existing system drive unusable. OF course, this is a non-issue if your goal is to reinstall your operating system from scratch.
Disabling Fast Startup
If you are attempting to load the firmware on a computer already running Windows, this might prove difficult because of the Fast Startup setting that might be enabled. Fast Startup was first introduced in Windows 8 as a way to make Windows start quicker after shutdown by caching key pieces of operating system code.
If you are experiencing problems loading your BIOS or UEFI or changing your boot order, start Windows then turn off Fast Startup.
- Press Windows key + X
- Click Power Options
- Click Choose what the power buttons do
- Click the link Change settings that are currently unavailable
- Under Shutdown settings, uncheck Turn on fast startup (recommended)
Boot Device Menu / Boot Override
Some computers will let you press a function key that takes you to a direct menu where you can immediately choose, which volume: USB thumb drive, SD Card, external hard disk, local disk or optical media you would like to boot from. Dell and HP systems, for instance, will present an option to boot from USB or DVD after striking the F12 or F9 keys respectively. This boot device menu is accessed once you’ve already entered into the BIOS or UEFI setup screen.
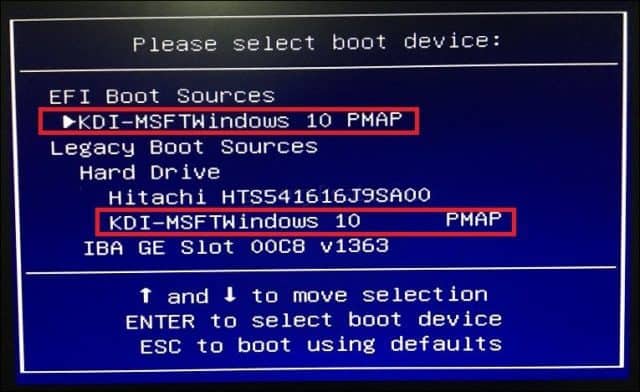

Here is a list of commands for accessing the direct boot menu on popular brands:
Brand | Command |
Acer | Esc / F9 / F12 |
| Asrock | F11 |
| Asus | Esc / F8 |
| Compaq | Esc / F9 |
| Dell | F12 |
| Fujitsu | F12 |
| Gigabyte | F12 |
| HP | Esc / F9 |
| Intel | F10 |
| Lenovo | F12 |
| MSI | F11 |
| Packard Bell | F8 |
| Samsung | Esc |
| Sony Vaio | F11 |
| Toshiba | F12 |
Microsoft Surface and Modern Windows 10 Devices
The Microsoft Surface uses its own unique interface for booting into the UEFI firmware interface.
First, you need to access your BIOS / UEFI setup utility on your Surface.
- Make sure your Surface or Surface Pro is fully powered down.
- Press and hold the volume up button located on the left side of the device.
- Press and hold the power button for five seconds located on the top of the device.
- Release the power button after five seconds but continue to hold down on the volume button until you see BIOS UEFI.
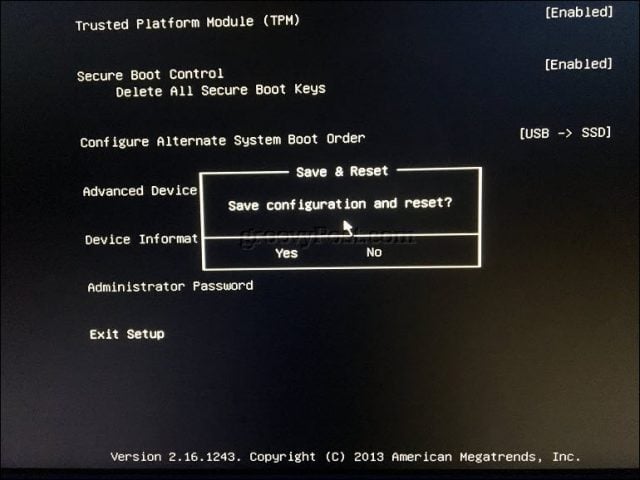
The Surface uses a combination of text-driven interface, touch, and mouse input to modify boot settings. Navigate down to the option Configure Alternate System Boot Order using the down arrow key. Hit the Enter key, which will load a submenu; use the up and down arrow to select the first boot device then hit Enter.
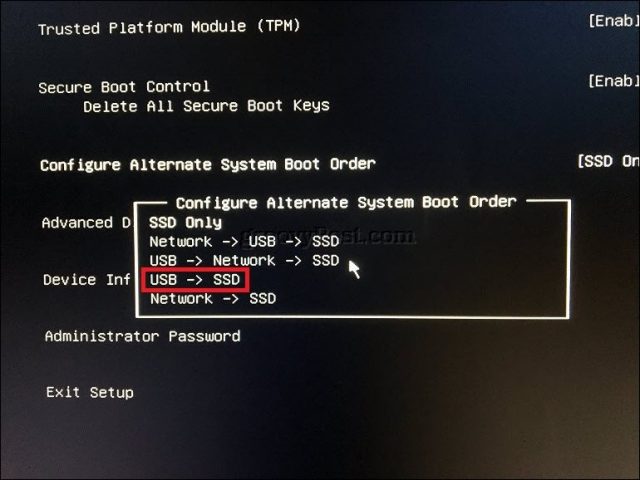

Navigate down to the Exit setup menu, hit Enter, use the left or right arrow keys to select yes then hit Enter.

Configuring UEFI on Windows 8 or Windows 10 Computers
If your computer or device is already running an existing version of Windows 8 or Windows 10, you might be able to initiate booting from removable storage from within the operating system. Click Start > Settings > Update & security > Recovery. Then, under Advanced startup, click Restart now.
If this option is not available, sign out of Windows 10, then hold down the shift key, click the Power menu, then click Restart. Continue to hold down the shift key then wait until the Recovery environment is loaded. The Choose an option menu lets you access and boot from removable media attached to the system.
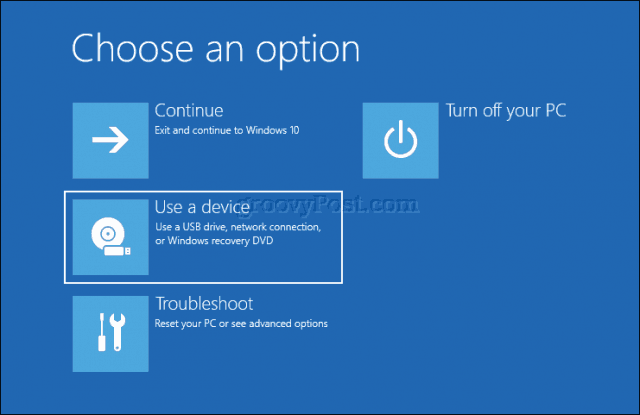

If you need to access advanced boot options, click Troubleshoot, then click the UEFI Firmware Settings to make further changes.


What About Mac?
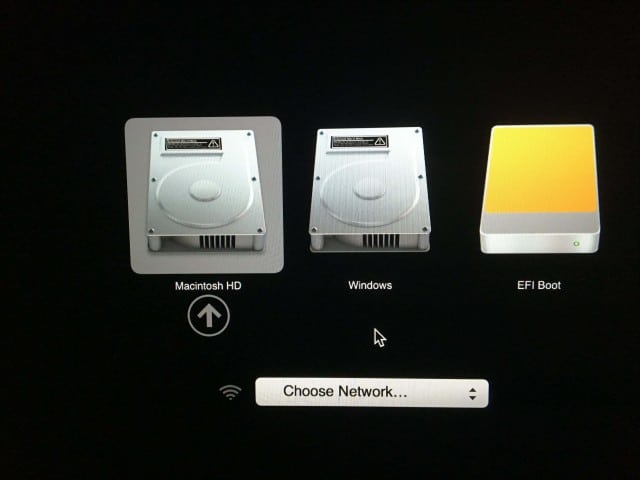
For the past 10 years, Apple Intel-based Macintosh computers have supported Windows. Most Macs will allow you to boot from a CD by pressing and holding C on startup. Booting an operating system other than OS X or macOS from a USB drive is a little more involved. We previously covered preparing your Mac for installing Windows 10 using the Boot Camp wizard in macOS. After preparing your boot camp partition and install media, booting from it is as simple as holding down the Option key before you hear the startup chime.

Conclusion
One of the lessons users will learn from this is that not all computer configurations are alike, even if they are from the same brand. Hopefully, reading through this guide has given you enough background knowledge about the process to help you configure your particular system, or at least ask the right questions if you run into trouble.
Let us know what you think in the comments. If you don’t see your specific computer model or make described in this article, let us know so we can find it for you.
30 Comments
Leave a Reply
Leave a Reply

Robert Brown
January 17, 2017 at 10:14 am
Definitely one of the most useful recent groovyPosts.
Now that very large (e.g., 128 and 256 GB) thumb drives are available,
how about a related article on how to create a bootable thumb drive as
a backup for a currently functioning Windows 10 system…in case the
system’s hard drive or ssd drive fails. Assume that the user never had
a Windows 10 installation CD because the system either came with
Windows 10 already installed or was upgraded via the (now expired)
free upgrade program.
Andre Da Costa
January 17, 2017 at 3:33 pm
Thanks Robert, will add it to my list of content ideas. If you are running Windows 10 Pro, there is already a solution in Windows to Go. I believe a third party option for Windows 10 Home is Rufus.
Prince Cyril
April 7, 2022 at 10:01 pm
Thanks so much everything you’ve explain is what I’m facing now
Mike Ragsdale
January 30, 2017 at 5:50 pm
Great stuff. Any way to get this as a PDF as I’d love to save it.
Thanks,
Mike
Andre Da Costa
February 5, 2017 at 11:44 am
Click the PDF icon at the top of the article.
Steve Krause
February 6, 2017 at 8:03 am
Hi Mike,
Thanks for reading! Glad you enjoyed the article.
Good, bad news on your question.
Saving articles as PDF files here at groovyPost is possible however only those who donate or support the blog have the feature available. You can read more about it here:
https://www.groovypost.com/support-us/
The program helps support our small community here at gP.
Thnx,
-S
groovyPost.com
Casper
September 19, 2022 at 4:04 pm
I have a gateway gw series notebook with a single board that someone changed my password on. Is there a way I can jump the bios? There’s no cmos battery that I can find on the board and no way to disconnect the USB because they are built in to the device
Steve Krause
September 20, 2022 at 10:43 am
If it were me, I would contact Gateway Tech Support and ask them what the next step would be to get into the system.
Casper
September 21, 2022 at 2:36 am
I already did and they want me to send it in on my warranty but with the info on my laptop I’m not willing to do that because it’s a security risk to other people’s data. I understand they are a business and they should be honest and trustworthy but I’m not putting other people’s info in the hands of someone else unless I can be right there to watch.
boity
April 6, 2017 at 10:08 pm
Hi guys, I was not aware of the UEFI configs so after trying to boot my Packard laptop from USB/DVD drive and had an issue of the laptop only displaying the HHD on the boot option no matter how good I configured the BIOS. I then opened the laptop,took the HDD and formatted it using my desktop, what I noticed is that I deleted the recovery and security partitions that were on the HDD.so now when put the HDD back to the laptop the laptop says no bootable device.it does not display any of the three “HDD,USB,DVD ROM” which I think it uses UEFI settings that were on tone of the partitions that I deleted from HDD.is there a way to get the UEFI to the partition or fiddle with the bios to end up installing windows or any other way please help
Bruce Lightfoot
April 27, 2017 at 7:24 am
have seen noted either here or elsewhere that part of your problem may be the missing partitions. Not the content, but the lack of those partitions. Your BIOS / UEFI routine is looking for the bootable drive to be whatever partition Number that your C:\ drive used to be. Try to recall what was there before the drive was wiped. Then use some drive partitioning software to add back in the missing partitions – ahead of what you have now. You may have to move the C: partition to make room, but the partitions you are adding can be small, but they have to be there.If you had, say, two partitions ahead of your old C:\ drive, your boot routine will be looking for the third partition to be the bootable one. I have found that one of the most valuable things I can do before changing or updating a drive is to go into Control Panel > Admin Tools >Computer Manager > Storage > Disk Manager and take a screen shot of the drives and their partitions and save that to a flash drive for future use.
My current furball is a 5-year old laptop with a tiny 20GB SSD plus a boot drive with 5 partitions. Cloning that Win 10 / UEFI mess to a replacement drive when the boot drive has quite a few bad sectors is thoroughly non-trivial! The steps above are a definite help.
Tom Pagh
April 18, 2017 at 6:25 am
Question: On a custom built desktop that was upgraded to Win-10, is it possible to change the BIOS to UEFI? I have been trying to get hyper-D to work but receive error that no UEFI located.
Steve
April 20, 2017 at 6:34 am
I am trying to get an image on to a corrupt Hannspree mini PC – With UEFI BIOS
F2 fails to do anything – so how do I set the boot to either DVD drive or flash drive via USB Port ?
John Ford
April 28, 2017 at 7:24 am
Great post but thought I’d mention that later Toshiba laptops (mine is an R50B) need f2 held down while powering onto get into the setup.
Andre Da Costa
May 2, 2017 at 6:51 pm
Thanks John! Thats why we love when our readers chime in the comments. :)
john g
July 21, 2017 at 5:09 pm
installing windows 8.1 or 10 on a mac via usb will not install normal sound drivers because of EFI boot
hopeful
July 27, 2017 at 10:28 am
I hope this is the right forum for the following.
I have experienced a viral spyware attack in which they, whoever that is, started to delete files from my windows 10 hard drive before my very eyes. I immediately shut off my 2 pc’s. They contain files valuable to me which I want to preserve.
My strategy to recover from this attack is to boot up with Linux from a usb drive.
Then create a clone image of the hard drive and store that on an external hard drive purchased for this purpose. I would then convert the machine to 100% Linux hopeful that I will prevent further attacks. So my first question, “Is this a good strategy?”
However in attempting to boot from the usb I find myself blocked. I click F2 on the load and it shows only one boot option, windows on the hard drive. I am using a Dell Inspiron. So I click on the reset options button and up pops a nice list of options with USB first. So I click on USB, enter the three lines of information including a reference to the live Ubunta USB flash drive I intend to use, and up pops a single line containing the USB directive at the end of the line, but at the beginning is the hard drive again. They are together as single choice. Clicking on F12 during startup shows a boot list with only one option, the hard drive. So I am guessing that whatever file contains the boot options has been maliciously altered. I have been researching the above and must say the situation is complex.
Any good suggestions anyone?
Thanks
hopeful
Steve Krause
July 27, 2017 at 11:28 am
Hey there – Yeah, the comments section isn’t a great place for troubleshooting. My suggestion is to re-post your problem/question in our Free Forum here: https://forum.groovypost.com.
Thanks!
Claude
August 29, 2017 at 7:48 am
Hey there,
I try to boot from the USB key. The UEFI Bios not recognize the USB booting. Is only show my 2 hard drives.
How to setup the bios to recognize my USB key ?
Thank you
Claude.
Adam
October 18, 2017 at 1:21 am
I have an Asus tp200sa I need to install windows USB, somehow… Fresh start it had 10 on there and the update crashed it. Can’t figure it out for the life of me
jansteytt
October 27, 2017 at 3:38 pm
I am not sure I fully understand your question. Is it that your laptop was crashed by an update?
If that is so, there are several solutions. I suspect that your question should have been posted here https://forum.groovypost.com. One solution is to create a boot USB drive like System Rescue CD (use rufus to burn the ISO to your flash drive) then use the instructions in the article to boot the computer and do a boot repair.
colesen
January 8, 2018 at 10:52 am
I run a new Dell Inspiron laptop bundled with Windows 10 onto which I let Fedora 27 install itself for a dual boot system. The result is a system where UEFI boots the Fedora boot manager Grub which in turn presents a Fedora menu from which to select which OS to run – Fedora or Windows. I’m puzzled as to why not leave that job to UEFI? It knows which partitions are bootable and could at run time present a menu like that which Fedora presents of which OS to run namely without first having to hit a Fn key every time. In short, the user presses the power button for start and the next thing that happens is that UEFI present a menu of bootable systems found from which the user can select the one desired. Thus leaving no need for Grub to know about Windows.
Michael Brininstool
January 8, 2018 at 7:46 pm
I could really use some help. I have made a Windows 7, 32-bit, bootable disk on an SD Card. My goal is to use this SD card as the system disk instead of any internal hard disk or SSD. I want the computer to start and run off of the SD card and internal ROM and RAM only. I set the BIOS boot order to have the computer boot from the SD card, but it then wants me to install the operating system onto another disk. Why does the computer not just install the operating system into ROM/RAM during initial start up and allow me to use the computer? Please help.
michael clyde
December 25, 2019 at 4:52 am
What exactly do you mean “I have made a W7, 32bit, bootable disk on an SD card”?
Do you mean you have burned the ‘Install Files’ (from an .iso file/what’s on an installation disk) onto an SD card?
” I want the computer to start and run off of the SD card and … ”
“I set the BIOS boot order to have the computer boot from the SD card, but it then wants me to install the operating system onto another disk.”
Are you trying to use the SD card like you would a faster USB Flash Drive in a “Windows-To-Go” type of setup?
Mrs_D
April 10, 2018 at 6:46 pm
Hi, I have an HP desktop computer with UEFI, although my system has Win7 64-bit. I read up about how to start from the BD-ROM (Blu-Ray), and it said that you press ESC to get the Startup Menu, then F9 to get the Boot Options Menu. I read some solutions that said you had to disable the Secure Boot to startup from DVD, but I run a program called Belarc Advisor to give me system information, and it reported that the Secure Boot was laready disabled—possibly that is because Windows 7 uses the legacy options??
You were supposed to be able to change the boot order on a temporary basis. I booted from a bootable DVD (Acronis Recovery environment), and the BDDVDRW CH30L drive did show up under the UEFI devices, second after Windows Boot Manager. (My two other nonbootable USB drives also showed up under Legacy devices.) I used the arrow keys to navigate to the BDDVDRW device and pressed Enter to select it. It started up just fine, and I was able to use the Recovery Software on the disk to look at the USB drives and list which backups were available.
Then I opened the BDD tray, put in another bootable disk I wanted to take a look at, and restarted the computer. When I pressed ESC, then F9 to go into the Boot Options Menu, the BDDVDRW drive no longer shows up—only Windows Boot Manager. I have tried going into Windows and back out, etc. Nothing seems to work to make the BDDVDRW listed again! Belarc Advisor reports that Secure Boot is still disabled, so nothing has changed there.
Any ideas on why the menu has changed? Or how I can enable the device to come up before Windows Boot Manager as a permanent option?
Thanks for any advice.
Jess
September 28, 2018 at 10:31 pm
Hi so I currently have a windows surface pro was previously running on windows 10 and I’m just trying to do a clean install I’ve already done the media install on a usb but when I go to the boot menu I don’t get an option to even be able to configure an alternate system boot order. Please help I just want to be able to print again
Mergatroid
May 17, 2019 at 8:01 am
I have been using flash drives created with the Microsoft Media Creation Tool (MCT) to install Windows 10 on client’s PCs.
Whenever there is a semi-annual major update, I like to recreate the flash drive so I don’t have to download so many updates after the installs. I have found that many flash drives fail for no particular reason. The MCT will fail at the end of the process without any explanation.
Doing internet searches I found information saying that this could happen if there is a MBR present on the flash drive, so I started removing all the partitions before running MCT. This has been OK so far on a good quality flash drive (Patriot), but it seems to have caused a problem on some less expensive flash drives. A couple have failed completely, a couple more just will not work with the MCT even after deleting all the partitions. These drives work for all other purposes.
So, I decided to get a SD card reader (I got a Kingston reader that has always worked great for me at home). This lets you plug a uSD or SD or both cards into the reader, and then you plug the reader into a USB port. I tried using the MCT, but it again gets a failure at the end with no explanation.
I downloaded the newest version of Rufus, and set it up for UEFI using a Windows 10 ISO I downloaded using the MCT. This worked perfectly on one of the cheap drives that previously failed using the MCT. However, when I use the SD card and reader in exactly the same way, tested on a Dell PC, it does not recognize the SD card as UEFI, but only as Legacy.
I had this same issue when I tried a slightly older version of Rufus. It seems it works properly on a real flash drive, but not quite on an SD card.
Any ideas on how to get a UEFI boot to work using an SD card? Could this be caused by the Kingston card reader?
michael clyde
December 25, 2019 at 10:38 pm
Hello,
Out of curiosity, is the Kingston Reader ‘Gold’ in color and USB (3.0/3.1 Gen 1/5Gbs) specification? Both of mine handle this so … .
Is the SD card formatted as FAT32?
Have you tried d/l the .iso file with something other than the MCT?
M$ suggest using something other than the MCT to create a USB suitable for a Legacy install with a W10 version released after 2016 or so, IIRC.
Does your Dell recognize the SD card and K reader in any other view/type?
It shouldn’t matter but have you tried a different card?
I was born at night and even though it wasn’t 2-night, I could be way off the mark.
G/L,
michael clyde
John H
November 29, 2021 at 11:54 pm
Hello,
Great post. However, old, non-tech guy here who is confused. I’ve got a boxed retail copy of 10 Pro. I want to load it onto an older Dell XPS i7 that currently has a copy of Win 7 on one partition and a copy of Win 10 home that is NOT activated on another partition of the SSD. (Un activated because MS wouldn’t let me have a free upgrade because the Win 7 came pre-installed on the Dell!) So, I bought this retail boxed copy of Win 10 Pro that comes with an MS USB thumb drive. The instructions for installation are pretty straight forward: Turn on computer, install USB drive, navigate to it, click setup.exe and follow on-screen instructions. Naturally, this doesn’t work. What I seem to get is a re-install of Win 10 Home (still un-activated and not soliciting the key that came with the boxed Pro! Is this because the simple instructions somehow don’t apply in my case and I need to boot from the USB drive as outlined in this post?
Bruce McBain
May 9, 2022 at 6:57 am
Dear Sirs and Madams, in the “start your computer” stage, you wrote: “Start your computer then proceed to strike the appropriate key or command to load the BIOS.” I am not trying to be obtuse but when should the user “proceed to strike” (not “press” but rather “proceed to strike”) the appropriate key? Immediately? After a few seconds? After the computer has started? And press -oops- “proceed to strike” once?, repeatedly?, hold down the key during start up? And one further question, in many cases two or three keys are indicated, such as F2/delete. Does that mean (a) proceed to strike both (b) proceed to strike them in sequence? (c) proceed to strike either?
Thank you for clarifying the above when you have time.